
13 Minutes
Understanding the Concept of an AI Agent
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a transformative force across various sectors, from healthcare to finance, and its evolution continues to fascinate both the tech industry and the public. At the heart of this evolution are AI agents, a concept that might seem straight out of science fiction but is increasingly becoming a reality. This blog post delves into what AI agents are, their types, applications, design principles, and the challenges and limitations they face.
An AI agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions to achieve its objectives. It is a key concept in artificial intelligence that has been studied extensively in fields such as machine learning, robotics, and cognitive science. AI agents are designed to be autonomous, intelligent, and adaptive, allowing them to operate in complex and dynamic environments.
An AI agent consists of a set of sensors that gather information from the environment and a set of actuators that allow the agent to interact with its surroundings. The agent also has a decision-making mechanism, which is typically based on machine learning algorithms, that determines the best course of action based on the information gathered by the sensors.
Key Components of AI Agents
Sensors and actuators are the key components that allow AI agents to interact with their environment. Sensors gather information about the agent’s surroundings, such as the position and orientation of objects, the temperature and humidity of the air, or the presence of obstacles. This information is then processed by the agent’s decision-making mechanism to determine the best course of action.
Actuators, on the other hand, allow the agent to interact with its environment by performing physical actions. These actions can include moving the agent’s body, manipulating objects, or communicating with other agents or humans. Actuators can take many forms, such as motors, speakers, or displays, depending on the specific application of the agent.
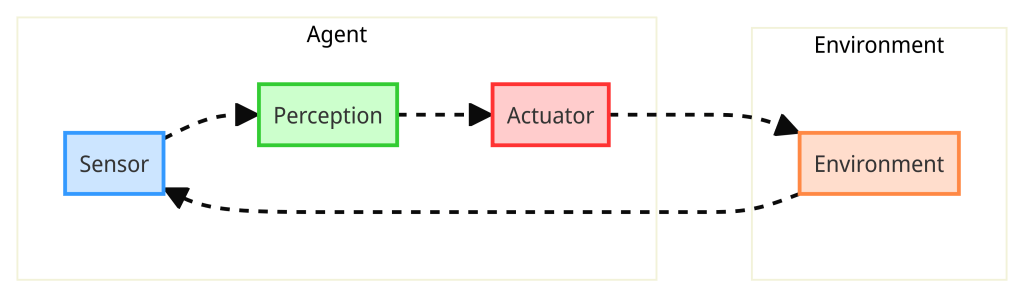
Perception, a combination of sensors and actuators allows AI agents to perceive their environment, reason about it, and take actions to achieve their objectives. For example, a robot vacuum cleaner might use sensors to detect the presence of dirt on the floor and actuators to move its cleaning brush and suction mechanism to remove the dirt.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensors | Devices that gather information from the environment, such as cameras, microphones, and touch sensors. |
| Actuators | Devices that allow the agent to interact with its environment, such as motors, speakers, and displays. |
| Decision-making mechanism | The algorithms and software that determine the best course of action based on the information gathered by the sensors. |
| Perception Module/Sensors | This component allows the AI agent to observe and interpret its environment through sensors such as cameras, microphones, or other data sources for capturing relevant information. |
| Reasoning/Decision-Making Module | This module enables the AI agent to make decisions and take actions based on the perceived information. It involves algorithms for problem-solving, decision-making, planning, and reasoning. |
| Learning Module | This component empowers the AI agent to improve its performance over time through experience, using techniques like machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning. |
| Action Module/Actuators | This module allows the AI agent to execute actions and interact with its environment through actuators, robotic arms, computer screens, or other output devices. |
| Memory Module | This component acts as the agent’s memory bank, storing information gathered from its surroundings and using these recorded memories to guide future actions and enable self-improvement. |
| Communication Module | This facilitates interaction between the AI agent and other entities, such as humans or other agents, through natural language processing, dialogue systems, or communication protocols. |
| Profiling Module | This module determines the agent’s function or role within its context, defining its purpose and scope of operation. |
| Planning Module | This module allows the agent to strategize and plan future actions based on its goals and the information it has gathered, enabling it to operate in dynamic environments. |
Key Takeaways: The specific components and their implementation may vary depending on the type of AI agent, its application domain, and the desired capabilities. However, these key components work together to enable AI agents to perceive, reason, learn, and act autonomously to achieve their goals.
The decision-making mechanism is the heart of an AI agent, as it is responsible for interpreting the sensor data and selecting the appropriate actions to take. This mechanism can be based on a variety of machine learning algorithms, such as neural networks, decision trees, and reinforcement learning.
Types of AI Agents
There are several different types of AI agents, each with its own unique characteristics and applications:
| Agent Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Reflex Agents | Act solely based on the current percept from the environment, following a condition-action rule without any memory or internal model of the world. Suitable for simple environments with straightforward rules. |
| Model-based Reflex Agents | Have an internal model of the environment and use it to make decisions, considering the potential future consequences of their actions. Can handle partially observable environments. |
| Goal-based Agents | Have specific goals or objectives they aim to achieve. Reason and plan a sequence of actions to reach their goals, considering the current state and potential future situations. More flexible than reflex agents. |
| Utility-based Agents | Make decisions based on a utility function that maps a situation to a measure of utility or preference. Choose actions that maximize their expected utility or reward. Well-suited for environments with uncertain or stochastic outcomes. |
| Learning Agents | Can improve their performance over time by learning from experience and adapting their behavior accordingly. Use machine learning techniques like reinforcement learning to optimize their decision-making process. |
| Hierarchical Agents | Organized in a hierarchical structure, with higher-level agents decomposing complex tasks and delegating subtasks to lower-level agents. Allows for efficient coordination and problem-solving in complex environments. |
| Multi-agent Systems | Involve multiple agents working together, either cooperatively or competitively, to achieve individual or collective goals. Require communication, coordination, and negotiation between agents. |
Examples of Sensors Used in AI Agents
AI agents can use a wide variety of sensors to gather information about their environment. Some common examples include:
| Sensor Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| Cameras/Visual Sensors | Object detection, facial recognition, scene understanding, used in self-driving cars, robots, surveillance systems |
| Microphones/Audio Sensors | Speech recognition, voice commands, sound event detection, used in virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri |
| Touch/Tactile Sensors | Detect physical contact, pressure, texture, used in object manipulation and haptic feedback in robots |
| Accelerometers/Motion Sensors | Detect acceleration, tilt, vibration, movement, used in navigation, activity recognition, gesture control |
| GPS/Location Sensors | Provide location and positioning data, used in autonomous vehicles, drones, location-based services |
| Radar/LiDAR Sensors | Environment mapping, object detection, obstacle avoidance, used in self-driving cars, robotics |
| Temperature/Humidity Sensors | Monitor and respond to environmental conditions, used in smart home, agriculture, industrial applications |
| Biometric Sensors | Fingerprint, iris, facial recognition for authentication and identification, used in security and personalization |
| Wearable Sensors | Monitor vital signs and physical activity, used in healthcare and fitness applications |
| Spectroscopic Sensors | Material analysis, chemical composition detection, quality control in manufacturing and agriculture |
Key Takeaways: These sensors can be used in a wide variety of applications, such as navigation, object recognition, and human-robot interaction. For example, a self-driving car might use vision sensors to detect other vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signs, while using GPS sensors to determine its location and route. A robot assistant might use auditory sensors to detect voice commands and touch sensors to detect when a human is interacting with it.
These sensors provide the necessary input data for AI agents to perceive their environment, enabling them to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions based on their goals and the specific application domain. The choice of sensors depends on the agent’s task, environment, and required capabilities.
Challenges facing Ai Agents
AI agents, while offering numerous benefits, face several significant challenges that need to be addressed to ensure their effective and ethical deployment. Here are some of the key challenges:
| Concern | Description |
|---|---|
| Bias and Fairness | AI systems can inherit and amplify biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, especially in areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Addressing these biases to ensure fairness is a critical ethical concern. |
| Privacy Concerns | AI agents require access to large amounts of data, including sensitive personal information. Managing the collection, use, and protection of this data to prevent privacy violations and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is essential. |
| Transparency and Accountability | Many AI algorithms, especially deep learning models, are “black boxes” that are difficult to interpret. This lack of transparency can undermine trust and make it hard to hold systems accountable. Developing explainable AI that provides insights into decision-making is crucial. |
| Security Risks | AI systems are vulnerable to security threats, including adversarial attacks that manipulate input data to deceive the system. Implementing robust security measures and monitoring for vulnerabilities are significant challenges. |
| Job Displacement | Automation through AI can lead to job displacement and economic inequality. Ensuring a just transition for workers, including reskilling and upskilling programs, is necessary to help them adapt to new job opportunities. |
| Ethical Dilemmas | AI raises complex ethical questions, such as the use of autonomous weapons, AI in healthcare, and potential replacement of human expertise. Developing ethical guidelines to ensure responsible AI use is critical. |
| Technical Complexities | Implementing advanced AI requires specialized knowledge in machine learning technologies. Integrating ML libraries with applications and training agents with enterprise-specific data can be technically complex, posing a barrier to effective deployment. |
| Data Quality and Availability | AI relies on large, diverse datasets for training. Not all industries have access to high-quality, unbiased data, which is essential for successful AI implementation. |
| Explainability | The complexity of AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, often makes their decision-making processes opaque. This can hinder trust and accountability, especially in critical areas like healthcare and law enforcement. |
| Environmental Impact | The computational resources needed to train and run AI models can have a significant environmental impact. Minimizing AI’s carbon footprint and promoting sustainable AI development are important considerations. |
Key Takeaways: Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach involving technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and society at large. Developing ethical guidelines, regulations, and best practices is essential to ensure that AI technologies are developed and deployed in ways that benefit humanity while minimizing potential harms.
Real-world Applications of AI Agents

AI agents find applications across a broad spectrum of domains, demonstrating their versatility and transformative potential:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Business and Operations | From supply chain optimization to customer service and workforce planning, AI agents streamline processes and enhance efficiency. |
| Healthcare | AI agents assist in disease diagnosis and drug discovery, revolutionizing patient care and treatment strategies. |
| Autonomous Systems | In self-driving vehicles and robotics, AI agents navigate and interact with the environment intelligently. |
| Finance | AI agents transform trading systems and portfolio management, making data-driven decisions to optimize financial outcomes. |
| Gaming and Smart Environments | From creating challenging game AI to managing smart homes and traffic systems, AI agents contribute to more engaging and efficient environments. |
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are transforming various industries by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving user experiences. Here are several real-life examples of AI agents and their applications.
Examples of AI Agents in use today
| Field | Examples and Key Players | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Personal Assistants | Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant | Use NLP to respond to commands, manage schedules, set reminders, control smart home devices, and provide information. Learn from user interactions for personalized assistance. |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Tesla, Waymo | Navigate complex environments using sensor data, identify obstacles and ensure safe driving. Use deep learning to improve performance. |
| Customer Service Chatbots | Zendesk | Provide instant responses to queries, handle routine tasks, escalate complex issues to human agents. Use NLP to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. |
| AI in Gaming | AlphaGo, Deep Blue | Provide challenging opponents using advanced algorithms and deep learning. Analyze game strategies and enhance the gaming experience. |
| Healthcare AI Agents | IBM Watson Health | Assist in diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient management by analyzing medical data for personalized treatment insights. |
| Financial AI Agents | Fraud detection systems, Stock trading bots | Analyze datasets to identify patterns and make predictions, reduce fraud, optimize trading, and improve risk management. |
| AI in Content Creation | ChatGPT, Jasper.ai | Generate blog posts, articles, and other content. Create outlines, draft content, and optimize for SEO, reducing time and effort in content creation. |
| AI in Real Estate | Roof.AI | Match buyers with properties, automate lead generation, manage customer interactions, and analyze preferences and trends for personalized recommendations. |
| AI in E-commerce | Amazon | Enhance shopping experiences with personalized product recommendations, manage inventory, and optimize pricing strategies. Analyze customer behavior for tailored experiences. |
| AI in Software Development | GitHub Copilot | Automate code generation, debugging, and version control. Suggest code snippets, identify bugs, and manage code repositories to improve development processes. |
Key Takeaways: AI agents are revolutionizing various sectors by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and providing personalized experiences. From personal assistants and autonomous vehicles to healthcare and financial services, these intelligent agents are becoming indispensable tools in our daily lives and professional environments. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications and improvements in the capabilities of AI agents.
Conclusion
AI agents are a rapidly evolving field that has the potential to transform many aspects of our lives. As sensors and actuators become more sophisticated and decision-making algorithms become more powerful, we can expect to see AI agents playing an increasingly important role in areas such as transportation, healthcare, education, and entertainment. However, it is important to consider the ethical implications of AI agents and to ensure that they are designed and deployed in a responsible and transparent manner.
AI agents represent a significant leap towards creating intelligent systems capable of autonomous decision-making and action. By understanding the different types of AI agents and their applications, we can better appreciate their potential to revolutionize industries and improve our daily lives.
Thank you for reading my blog post! If you found this topic engaging, I invite you to explore more of my content on Decentralized Intelligence and dive deeper into similar topics.
Continue your journey…

Sources:
Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2021). Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (4th ed.). Pearson.
[1] https://www.bloggingpro.com/use-ai-to-write-blog-posts/
[2] https://contentoo.com/blog/how-to-use-ai-to-write-blog-posts/
[3] https://www.simform.com/blog/types-of-ai-agents/
[4] https://getgenie.ai/write-a-blog-using-ai-blog-post-writer/
[5] https://www.godaddy.com/resources/skills/write-blog-post-properly-using-ai
[6] https://yellow.ai/blog/ai-agents/
[7] https://www.copy.ai/blog/how-to-write-a-blog-post-fast
[8] https://andrewchen.com/ai-blogging/
[9] https://www.reddit.com/r/Blogging/comments/18165ua/what_do_you_think_of_using_ai_to_punch_up_your/
[10] https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/
[11] https://zapier.com/blog/ai-agent/
[12] https://blog.fabrichq.ai/exploring-ai-agent-examples-real-world-applications-and-use-cases-1c3b469944ef?gi=834ce5b71e47
[13] https://sidecarglobal.com/blog/beyond-automation-the-era-of-ai-agents
[14] https://myscale.com/blog/fascinating-examples-ai-agents-action/
[15] https://botpress.com/blog/real-world-applications-of-ai-agents
[16] https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2023/04/12/the-dos-and-donts-of-using-ai-to-generate-blog-content/?sh=58d5448565da
[17] https://sierra.ai/news/ai-agents-guide
[18] https://cloud.google.com/products/agent-builder
[19] https://www.devteam.space/blog/10-real-life-examples-of-artificial-intelligence/
[20] https://ai.stackexchange.com/questions/3243/what-are-some-examples-of-intelligent-agents-for-each-intelligent-agent-class
[21] https://annenberg.usc.edu/research/center-public-relations/usc-annenberg-relevance-report/ethical-dilemmas-ai
[22] https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence
[23] https://iac.gatech.edu/featured-news/2023/08/ai-ethics
[24] https://connect.comptia.org/blog/common-ethical-issues-in-artificial-intelligence
[25] https://www.symmetry-systems.com/blog/mitigating-risks-in-the-age-of-ai-agents/
[26] https://www.unesco.org/en/artificial-intelligence/recommendation-ethics/cases
[27] https://www.verdentra.com/article/how-ai-agents-are-reinventing-cybersecurity/
[28] https://www.claconnect.com/en/resources/articles/2023/ai-is-a-new-cybersecurity-risk-learn-how-to-help-protect-your-organization
[29] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8826344/
[30] https://community.openai.com/t/the-ai-agents-including-apis-should-have-a-minimal-knowledge-about-themselves/705079
[31] https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2020/10/ethical-concerns-mount-as-ai-takes-bigger-decision-making-role/
[32] https://www.securitymagazine.com/articles/100711-security-leaders-discuss-llms-that-may-present-security-concerns
[33] https://www.simform.com/blog/ai-agent/
[34] https://dataconomy.com/2023/07/06/challenges-in-artificial-intelligence/
[35] https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/ai-agents/
[36] https://www.malwarebytes.com/cybersecurity/basics/risks-of-ai-in-cyber-security
[37] https://www.oracle.com/artificial-intelligence/ai-model-training-challenges/
[38] https://kobedigital.com/ai-development-and-implementation-challenges/
[39] https://itrexgroup.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-challenges/
[40] https://www.forbes.com/sites/eliamdur/2024/01/24/6-critical–and-urgent–ethics-issues-with-ai/
Discover more from Decentralized Intelligence
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


The article on AI agents as the building blocks of tomorrow’s intelligent systems highlights the transformative potential of AI Agent Development. By focusing on advanced <a href=”https://www.planethive.ai/services/ai-agent-development”>AI Agent Development</a>, we’re paving the way for smarter, more adaptive technologies that will shape the future. This progress emphasizes the crucial role of AI agents in creating efficient and innovative solutions across various industries.
LikeLiked by 1 person
The blog post on AI Agents: The Building Blocks of Tomorrow’s Intelligent Systems highlights the pivotal role of AI Agent Development in shaping the future of technology. As these agents become increasingly sophisticated, they will revolutionize how we interact with machines and automate various tasks. Embracing this development is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in an AI-driven world.
LikeLike